

Many wrist fractures occur during contact sports or sports in which you might fall onto an outstretched hand - such as in-line skating or snowboarding.
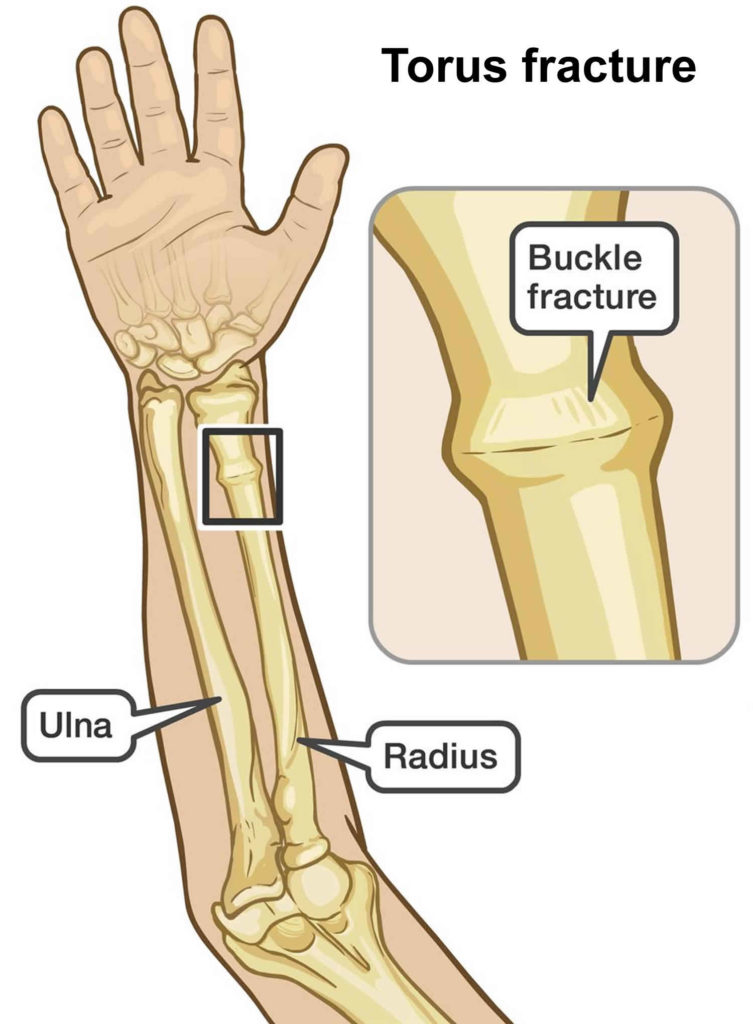
Falling onto an outstretched hand is one of the most common causes of a broken wrist. Distal radius fractures in the elderly population.

Distal radius fracture outcomes and rehabilitation. Non- or minimally displaced distal radial fractures in adult patients: Three weeks versus five weeks of cast immobilization-a randomized controlled trial. Epidemiological and treatment trends of distal radius fractures across multiple age groups. You can learn more about how we ensure our content is accurate and current by reading our editorial policy. Healthline has strict sourcing guidelines and relies on peer-reviewed studies, academic research institutions, and medical associations. Your surgeon may use various implants, such as rods, plates, and screws, to set the bone and allow it to heal. Severe fractures, such as open fractures where the bone breaks through your skin, may need surgical treatment. Reduction is when a doctor moves the bones back into the proper positions without making a surgical incision. If you have a displaced fracture, meaning your bones aren’t in the right position, your doctor may perform reduction before immobilization. A doctor may prescribe stronger pain medications, like codeine, for severe injuries. Pain medicationsįor minor fractures, a doctor may recommend over-the-counter pain medications, such as ibuprofen (Advil) or acetaminophen (Tylenol). This helps decrease pain and allows your wrist to heal without re-injury. Immobilizationĭoctors will immobilize your wrist by applying a splint or cast. Severe fractures may require reduction or surgery. Medical professionals can manage most distal radius fractures conservatively with a combination of pain medications and immobilization. How do you treat a distal radius fracture? The growth plate is the area near the end of the bone where the bone grows from. Salter-Harris type fracture: A Salter-Harris type fracture is a break of the growth plate in children.Greenstick and torus fractures: These fractures are partial fractures that occur in children.It often occurs with the dislocation of one of the wrist bones. Barton’s fracture: Barton’s fracture is a rim fracture, or a fracture that affects the outer edges of the radius.This usually occurs when the end of the ulna moves behind the radius. Galeazzi fracture-dislocation: Galeazzi fracture-dislocation is a break near the end of the radius with a distal radioulnar joint dislocation.Die-punch fracture: Die-punch fracture involves the lunate fossa, an indent at the end of the radius where it connects to a bone in your wrist called the lunate.Chauffeur’s fracture: Chauffeur’s fracture occurs in the radial styloid, the outer part of the radius closest to your thumb.It occurs around 1.5 inches from your wrist joint. Colles’ fracture: Colles’ fracture is the most common type of distal radius fracture.Some particular patterns of fracture occur frequently. In a 2016 study, researchers concluded that none of these classification systems are particularly useful for surgeons in guiding treatment. Medical literature has described more than 15 different classification systems for distal radius fractures over the last 70 years.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
